
How to Build an End-To-End ML Pipeline With Databricks & Aporia
This tutorial will show you how to build a robust end-to-end ML pipeline with Databricks and Aporia. Here’s what you’ll...
Aporia has been acquired by Coralogix, instantly bringing AI security and reliability to thousands of enterprises | Read the announcement
DataFrame is a two-dimensional data structure with labeled rows and columns. We can use the labels (i.e. index) to access a particular cell. Row and column indices can be considered as the address of a cell.
In this short how-to article, we will learn how to set the value of a cell in Pandas and PySpark DataFrames using the cell index.
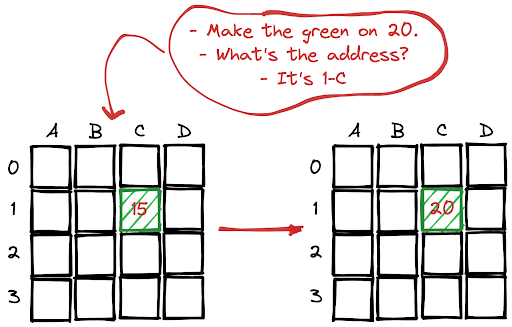
We can use both the loc and iloc methods for this task. Loc uses labels whereas iloc works with index values.
Consider the DataFrame shown in the above drawing. We want to change the value of the cell in green. Its address in terms of labels is “1-C”. In the case of using indices, the address is “1-2”
# with loc
df.loc[1, "C"] = 20
# with iloc
df.iloc[1, 2] = 20The row labels are the same as row indices unless we assign a customized index to the DataFrame.
We can use the collect method to get the value in a particular cell.
# with index
df.collect()[1][2]
15
# with labels
df.collect()[1]["C"]
15However, PySpark does not allow assigning a new value to a particular cell.

This tutorial will show you how to build a robust end-to-end ML pipeline with Databricks and Aporia. Here’s what you’ll...
Dictionary is a built-in data structure of Python, which consists of key-value pairs. In this short how-to article, we will...
A row in a DataFrame can be considered as an observation with several features that are represented by columns. We...

DataFrame is a two-dimensional data structure with labeled rows and columns. Row labels are also known as the index of...
DataFrames are great for data cleaning, analysis, and visualization. However, they cannot be used in storing or transferring data. Once...
In this short how-to article, we will learn how to sort the rows of a DataFrame by the value in...
In a column with categorical or distinct values, it is important to know the number of occurrences of each value....

NaN values are also called missing values and simply indicate the data we do not have. We do not like...